Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Its a way of making many copies of short stretches of a specific piece of DNA or RNA like a particular gene so it can be studied easily.
The heating cycles are what the PCR is as its a synthetic not found in nature process but your point is valid.

. This technique was developed in 1983 by Kary Mullis an American biochemist. Approximately how many copies of a single starting target sequence would be made after 8 cycles. Describe how polymerase chain reaction PCR works.
Describe how polymerase chain reaction PCR works. Once cooled the primers bind to one of the strands and the process of replicating starts with the help of the DNA polymerase. How does the polymerase chain reaction PCR work.
Polymerase chain reaction PCR is a laboratory technique that uses selective primers to copy specific segments of a DNA sequence. Simply put the PCR depends on the fact that DNA replication must begin with a primer a short piece of DNA or RNA that the DNA polymerase then extends. PCR is used to reproduce amplify selected sections of DNA or RNA.
Polymerase chain reaction is a technique used to target specific fragments of DNA and artificially amplify increase their quantity them. Describe how the polymerase chain reaction PCR works to amplify and copy DNA sequences. Sarah - The Polymerase Chain Reaction or PCR was dreamed up in the 1980s primarily by a scientist called Kary Mullis and is an absolutely fundamental tool in any molecular biology lab.
PCR testing allows researchers to make many copies of a small section of DNA or RNA in a. PCR or Polymerase Chain Reaction is a technique used in molecular biology to create several copies of a certain DNA segment. A strip of eight PCR tubes each containing a 100 μL reaction mixture.
A polymerase chain reaction PCR test detects genetic material from a pathogen or abnormal cell sample. PCR is based on using the ability of DNA polymerase to synthesize new strand of DNA complementary to the offered template strand. PCR has made it possible to generate millions of copies of a small segment of DNA.
Describe how the polymerase chain reaction PCR works to amplify and copy DNA sequences. The polymerase chain reaction PCR is a laboratory technique for DNA replication that allows a target DNA sequence to be selectively amplified. This tool is commonly used in the molecular biology and.
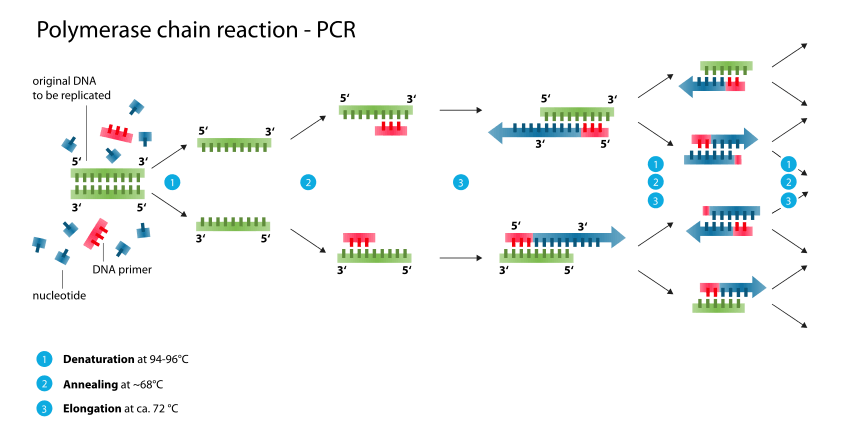
Heat is used to denature the DNA breaking hydrogen bonds in DNA. Double stranded DNA molecule is added to a tube of free nucleotides. Because significant amounts of a sample of DNA are necessary for molecular and genetic analyses studies of isolated pieces of DNA are nearly impossible without PCR amplification.
Explain the use of primers in PCR. PCR stands for polymerase chain reaction a molecular biology technique for amplifying segments of DNA by generating multiple copies using DNA polymerase enzymes under controlled conditionsAs little as a single copy of a DNA segment or gene can be cloned into millions of copies allowing detection using dyes and other visualization techniques. PCR Polymerase Chain Reaction is a revolutionary method developed by Kary Mullis in the 1980s.
Polymerase chain reaction PCR APBIO. This enzyme is often Taq polymerase an enzyme originally isolated from a thermophilic bacteria called Thermus aquaticus. Terms in this set 6 Step 1.
Is a scientific techniques in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence. Because DNA polymerase can add a nucleotide only onto a preexisting 3-OH group it needs a primer to which it can add the first. A DNA polymerase enzyme joins free DNA nucleotides together.
First step with the intitial mix is where there is an excess of Mg 2 ions Primers DNA nucleotides Template DNA Buffer and DNA Taq Polymerase 6 things. Invention in 1983 Using for making million billion copies of any part like DNA or gene copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes Tw. COVID-19 PCR tests use primers that match a segment of the viruss genetic material.
PCR is a technique that is used to take a gene of interest and amplify it through means of temperature and mixes containing crucial enzymes to allow the PCR technique to function. Answer- PCR- polymerase chain reaction. How does the polymerase chain reaction work.
IST1 EU IST1P LO IST1P1 EK A technique used to amplify or make many copies of a specific target region of DNA. This problem has been solved. During a polymerase chain reaction smaller segments of DNA are being copied.
This allows many copies of that material to be made which can be used to detect whether or not the virus is present. Sometimes called molecular photocopying the polymerase chain reaction PCR is a fast and inexpensive technique used to amplify - copy - small segments of DNA. Polymerase chain reaction PCR is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies complete or partial of a specific DNA sample allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it or a part of it to a large enough amount to study in detail.
Previously amplification of DNA involved cloning the segments of interest into vectors for expression in bacteria and took. Approximately how many copies of a single starting target sequence would be made after 8 cycles. The first stage of this process occurs when the DNA is heated to produce two single strands that are separated.
The order in which the free nucleotides are added is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in the original template DNA strand. The primer is an artificial strand of DNA that is made with a complimentary base sequence to the beginning of the DNA fragment to be amplified. PCR can use the smallest sample of the DNA to be cloned and amplify it to millions of copies in just a few hours.
PCR polymerase chain reaction is a method to analyze a short sequence of DNA or RNA even in samples containing only minute quantities of DNA or RNA.
Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Principle Procedure Types Applications And Animation


0 Comments